
Everything You Need to Know About MVP
When translating an idea into software, you do not always need to build a full-fledged product. Rather, a fail-proof method is building prototypes or a minimum viable product (MVP). This can help you identify whether your software product has any viable market demands and must-have features.
This means you can shape the software product as per the user needs and launch success in no time. Globally various software products like SaaS platforms, web apps, and mobile apps, have been launched as MVPs.
What is MVP?
MVP in software development stands for minimum viable product. This is the simplest version of any technical solution built with one or just a few functional features. It is built to test core features and gather feedback from early users before investing heavily in development. The goal is to launch quickly, validate the product concept, and iterate based on real-world usage.
Purpose: The primary objective of an MVP is to minimize the time and resources spent on building a product while still providing value to users.
Features: It consists of only essential features needed to fulfill the product’s core purpose and attract early adopters.
User Feedback: MVPs are designed to be tested by real users, allowing developers to gather valuable feedback about what works and what doesn’t.
Iteration: Based on user feedback, the MVP can be refined and expanded into a more complete product in subsequent iterations.
Benefits of MVP Development
1. Cost Savings
MVPs focus on core features, minimizing development time and resources. This advocates for lower costs compared to building a fully-featured product from the start. By testing ideas early, MVPs help avoid costly mistakes and wasted resources. In simple abc, you can ensure the end product resonates with the target audience.
2. Faster Time to Market
Focusing on essential features allows businesses to get their product to market faster, potentially gaining a competitive edge. MVPs enable iterative development, where the product is refined and improved based on user feedback, leading to faster product evolution.
3. User Feedback and Validation
MVPs encourage early user engagement. This empowers businesses to gather valuable feedback and identify areas for improvement. You can test business ideas and product concepts before making large-scale investments. This helps to determine if the product is truly viable.
4. Attracting Investors
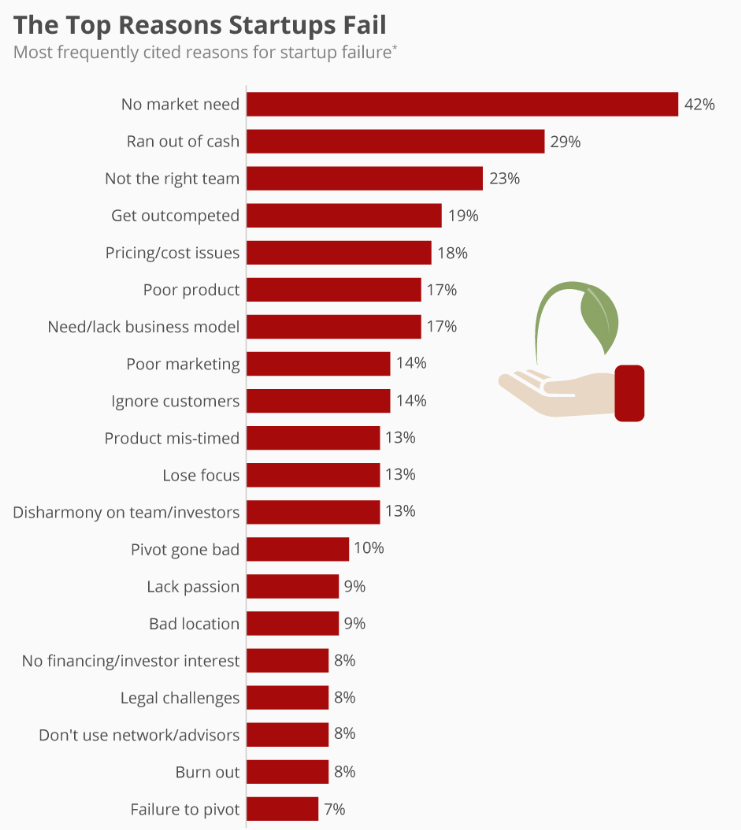
An MVP demonstrates that a team has a working concept and can attract early user feedback, which can be valuable for investors. Showcasing a functional product with early user engagement, MVPs attract potential investors. Nearly 42% of startups fail owing to zero market need and another 8% due to loss of the investors interests.
MVP software development helps to successfully escape such issues as you can test market needs with minimal investments.
5. Enhanced Focus and Efficiency
MVP boosts the core value proposition and essential features, reducing the risk of over-engineering or feature creep. This means prioritising most critical features and functions and allocating resources efficiently.
Why do you need to stay lean and agile with MVP software development?
Unlike full-fledged software, MVP development services are an iterative process. This means you test one assumption of the business model and launch it among the users for gaining feedback. These feedback are analysed to implement appropriate adjustments which are then released as iterations.
Lean or agile software development methodology helps to stay on track and make the most of the strategy. Staying lean and agile in MVP software development is crucial for maximizing value and minimizing risk.
It allows for faster time-to-market, data-driven decisions, and continuous improvement based on user feedback. This ensures the product aligns with market needs and reduces the cost of potentially unsuccessful features.
Guidelines for a successful MVP strategy
An MVP development agency can help you launch and refine quality software solutions. The focus is on prioritising user needs and iterative development. It involves defining the problem, understanding the target audience, identifying core features, and gathering user feedback for continuous improvement.
1. Define the Problem and Target Audience
- Clearly articulate the problem your product solves and the benefits it provides to users.
- Conduct thorough research to understand their needs, behaviors, and preferences.
- Develop detailed profiles of your ideal users. Keep the users at the forefront of the development process.
2. Focus on Core Features and User Needs
- Identify the minimum set of features needed to deliver a usable product. Address the primary user pain points with validated learning.
- Do not add unnecessary features.
- Implement a clear and intuitive flow with a friendly user interface.
3. Build, Test, and Iterate
- Don’t aim for perfection in the first version. Rather, launch a basic version.
- Actively seek feedback from users through surveys, interviews, and user testing.
- Continuously improve the MVP product based on user feedback and insights.
4. Track and Analyze Results
- Establish clear metrics to measure the MVP’s success, such as user acquisition rate, conversion rate, and retention rate.
- Use analytics tools to track user behavior and identify areas for improvement.
5. Continuous Improvement
- Keep up with market trends and competitor activities.
- Leverage as opportunities for learning and improvement.
- Embrace a mindset of continuous improvement and experimentation.
The Case Study of Uber MVP
Uber’s Minimum Viable Product (MVP), initially called UberCab, was a simple iPhone-only service. It allowed users to book black car rides in San Francisco. It focused on core functionalities like ride booking, GPS tracking, and fare calculation, proving the concept of a car-hailing app before scaling to a global platform.
- The founders, Travis Kalanick and Garrett Camp, initially tested the concept by offering the service to their friends and colleagues.
- Initially, the service was available through SMS, with users texting their pickup location to the platform.
- As demand grew, the founders expanded the service to other cities. Eventually they developed a mobile app for wider use.
- Uber used data from each ride to refine its service. This helped to improve routing and added new features like driver ratings and live tracking.
Conclusion
MVP lays the foundation for building best-in-class products with actual market demands. It also allows for early gathering of user feedback, optimizing the product, and potentially attracting investors.
At Coding Sprint, an software development company, we can help you build cutting-edge applications and release iterations that keep you ahead.

